[ad_1]
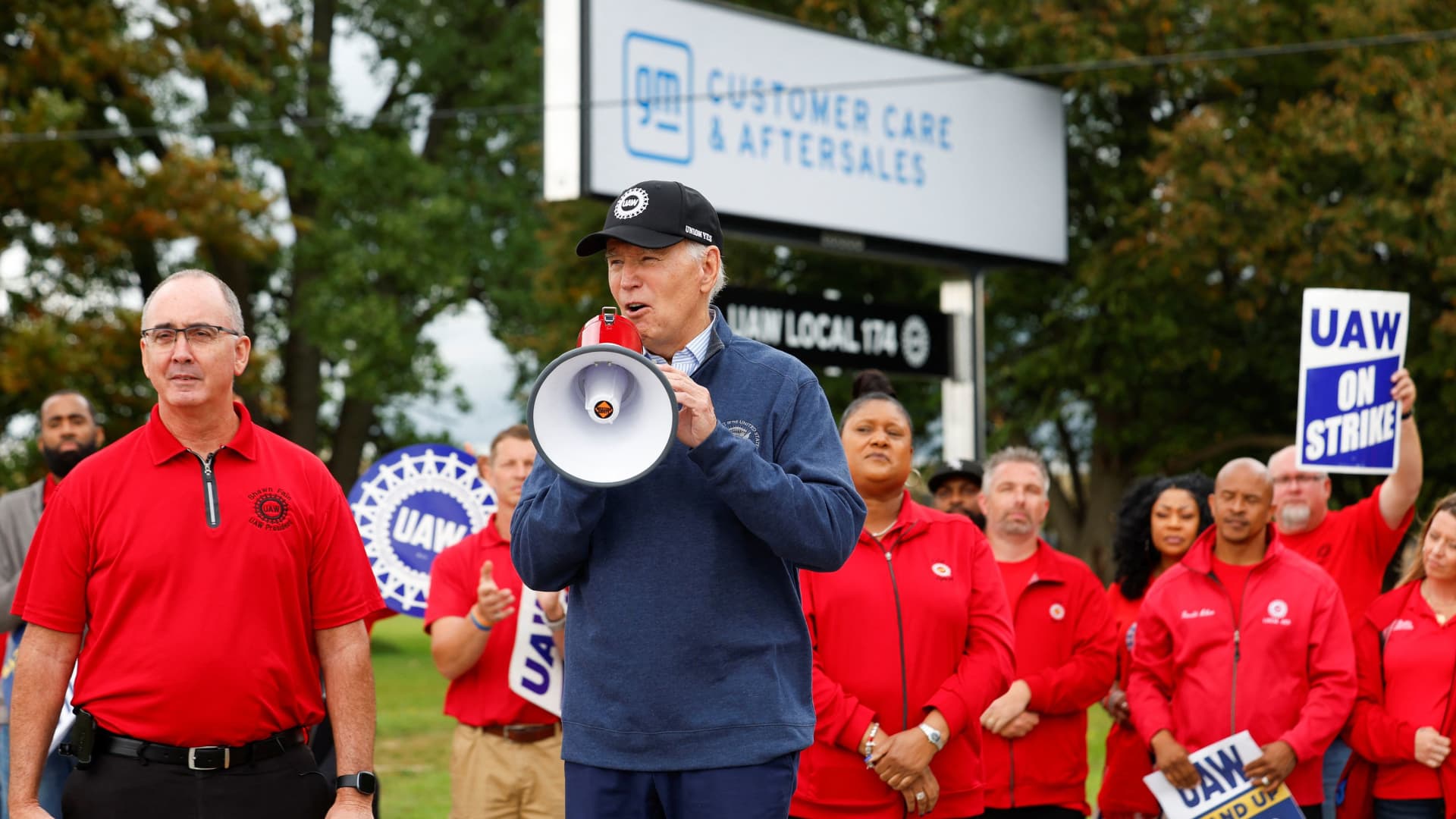
President Joe Biden speaks next to Shawn Fain, president of the United Auto Workers, as he joins striking members of the union on the picket line outside GM’s Willow Run Distribution Center in Bellville, Michigan, Sept. 26, 2023.
Evelyn Hockstein | Reuters
DETROIT — A tentative deal Monday between the United Auto Workers and General Motors brought an end to contentious negotiations and roughly six weeks of labor strikes against the Detroit automakers.
UAW President Shawn Fain warned of a more combative union heading into the talks, but not many, if anyone, expected the union to strategically outmaneuver the companies like it did, leading to record deals for 146,000 UAW members with GM, Ford Motor and Stellantis.
While full details of the finalized deals are still emerging, they set 25% compounded raises over the 4½-year agreements, including an 11% increase upon ratification; reinstatement of cost-of-living adjustments; increased 401(k) company contributions; and enhanced profit-sharing bonuses.
UAW members must still vote to ratify the tentative agreements. In the cases of GM and Stellantis, local union leaders must also approve the deals before member voting.
Fain and the union are clear winners at the end of bargaining, but others like Tesla and President Joe Biden may also come out ahead. Counted among the losers, then, are the automakers but also potentially their investors — and electric vehicle ambitions.
“There’s lots of winners in this. So No. 1, of course, are the UAW members,” said Art Wheaton, a labor professor at The Worker Institute at Cornell University. “It was way more than I expected and thought possible … It is a home run.”
Winner: Shawn Fain
Fain became the face of the UAW during the talks, utilizing wide-ranging talking points such as fights against billionaires, workers’ rights and rebuilding the middle class to successfully bring national attention to the union’s talks with the Detroit automakers.
Thanks to his tough rhetoric and frequent live updates during the process, Fain is the face of the victory, too.
Loser: Big Three
The “Big Three” Detroit automakers underestimated Fain and the union’s strategy, which involved unprecedented, targeted strikes that kept the automakers on edge and helped to give the union leverage over the companies.
The result was record contracts for union employees that squeezed more out of the companies than many anticipated leading into the talks.
Potential winner: UAW organizing
Fain said Sunday the UAW plans to use these record deals to assist in its embattled organizing efforts, including at auto companies outside of the three Detroit automakers, citing talks with the “big five or big six” automakers.
Whether the UAW can organize foreign automakers in the U.S., also known as transplants, or electric vehicle companies such as Tesla or Rivian, will be determined in the coming years.
“They have the best chance now that they’ve had an over 40 years to organize the transplants and, perhaps, the nonunion electrical vehicle companies,” said Marick Masters, a business professor at Wayne State University in Detroit. “But it’s still a steep, uphill battle.”
Loser: Investors
Since the targeted strikes began Sept. 15, shares of Ford are down by 23%, GM is off by roughly 19%, and Stellantis, which has yet to release expected strike costs, fell about 4%.
It’s not immediately clear how much the deals will increase labor costs for the companies, which had argued that giving in to all of the union’s demands would affect their competitiveness and even long-term viability.
Deutsche Bank recently estimated the overall cost increase of the agreement at Ford to be $6.2 billion over the term of the agreement, $7.2 billion at GM, and $6.4 billion at Stellantis.
Ford said the UAW deal, if ratified by members, is going to add $850 to $900 in costs per vehicle assembled. Finance chief John Lawler last week said Ford will work to “find productivity and efficiencies and cost reductions throughout the company” to deliver on previously announced profitability targets.
Some winners, some losers: UAW members
Broadly speaking, the UAW members covered by the new deals are winners, however not everyone faced the financial toll of the union’s strikes against the Detroit automakers.
The union gradually added plant strikes as part of its targeted, or “stand-up,” strike strategy. That means members who were part of the initial strikes or were laid off due to the work stoppages were not paid beyond $500 weekly strike pay for nearly six weeks, while others were never called on to stop working.
Under the Ford deal, workers will be paid retroactively for hours worked on and after Oct. 23.
Potential loser: Nonunion plants
Nonunion plants from auto companies ranging from Tesla and Rivian to Toyota and Hyundai may be rethinking their pay structures for plant workers.
With the UAW’s record wins, such companies risk losing workers to their Detroit rivals’ plants. They may also be targets of increased organizing efforts by members seeking better wages like those for UAW members.
“By having the UAW win huge gains at their plants, now the nonunion companies have a choice: You either raise your pay and benefits to keep up with what the current rate is for the UAW or you face the chances of getting a union organizer and driving your plans,” Wheaton said.
Loser: EVs
To offset rising labor costs and address slower-than-expected demand for electric vehicles, Ford and GM each announced delays in production or investments for EVs.
GM has said it would delay at least three models in addition to expanding electric truck production by at least a year in Michigan until late-2025, while Ford said last week it would postpone $12 billion in planned spending on new EV manufacturing capacity.
Stellantis, which has invested heavily in plug-in hybrid electric vehicles for the U.S., has not announced any significant changes to its EV plans.
“Clearly the union came out ahead,” Masters said. “Companies will be able to survive the strike and be able to survive the rise in labor costs. But I’m not certain about whether or not they’re going to win competition for electrical vehicles.”
Potential winner: Tesla
The slower rollout of some EVs could allow Tesla more time to compete in the market with its current and upcoming products.
EV leader Tesla’s market share has declined in recent quarters amid increased competition, specifically in luxury vehicles, and the Detroit automakers were expected to increase competition in lower-priced models.
“It remains to be seen whether or not [the Detroit automakers are] going to be able to enter the fray with profitable vehicles, electric vehicles, in time to beat the competition and remain profitable on a scale that will enable them to endure as stand-alone entities do,” Masters said.
Winner: Biden
In a historic move, Biden decided to walk a picket line with UAW members to show his support and back up his self-proclamation of being the “most pro-union president in American history.”
While the UAW has withheld its re-endorsement of Biden so far, the support may sway the union to eventually do so. It also could sway critical blue-collar voters in the Midwest ahead of the 2024 presidential election.
Biden applauded the UAW’s deals with the Detroit automakers after speaking with Fain on Monday.
“These record agreements reward autoworkers who gave up much to keep the industry working and going during the financial crisis more than a decade ago,” Biden said at the White House. “These agreements ensure that the Big Three can still lead the world in quality and innovation.”
[ad_2]